Description
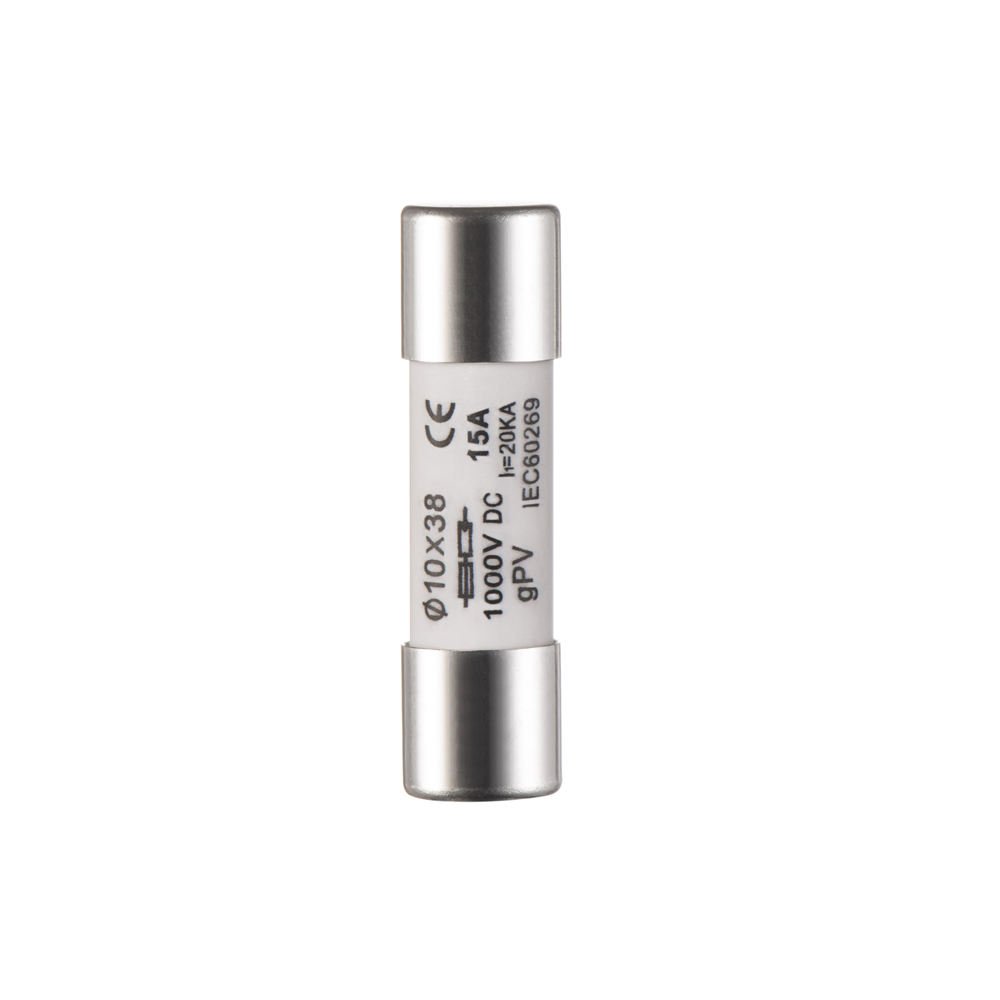
– A cylindrical fuse is a type of electrical fuse, shaped like a cylinder, designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrents.
– They are commonly used in various applications, from residential to industrial, and are known for their compact size and reliable performance.
– Cylindrical fuses are available in different sizes, voltage and current ratings, and breaking capacities.
– They are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity during overloads or short circuits, preventing damage to equipment and ensuring safety.
Key Features:
Shape and Construction:
Cylindrical fuses consist of a fuse element, typically made of a metal with a specific melting point, encased in a cylindrical cartridge, often made of ceramic or epoxy glass.
Function:
When the current flowing through the fuse exceeds the rated limit, the fuse element melts, breaking the circuit and preventing further damage.
Applications:
They are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Residential electrical panels.
Industrial control systems.
Protection of primary and secondary circuits.
Protecting power semiconductors (like those in solid-state contactors or converters) according to MISUMI Thailand.
Ratings and Specifications:
Cylindrical fuses come in various sizes, voltage ratings (e.g., up to 660V), current ratings (e.g., up to 32A), and breaking capacities. They are manufactured to meet specific standards like IEC 60269.
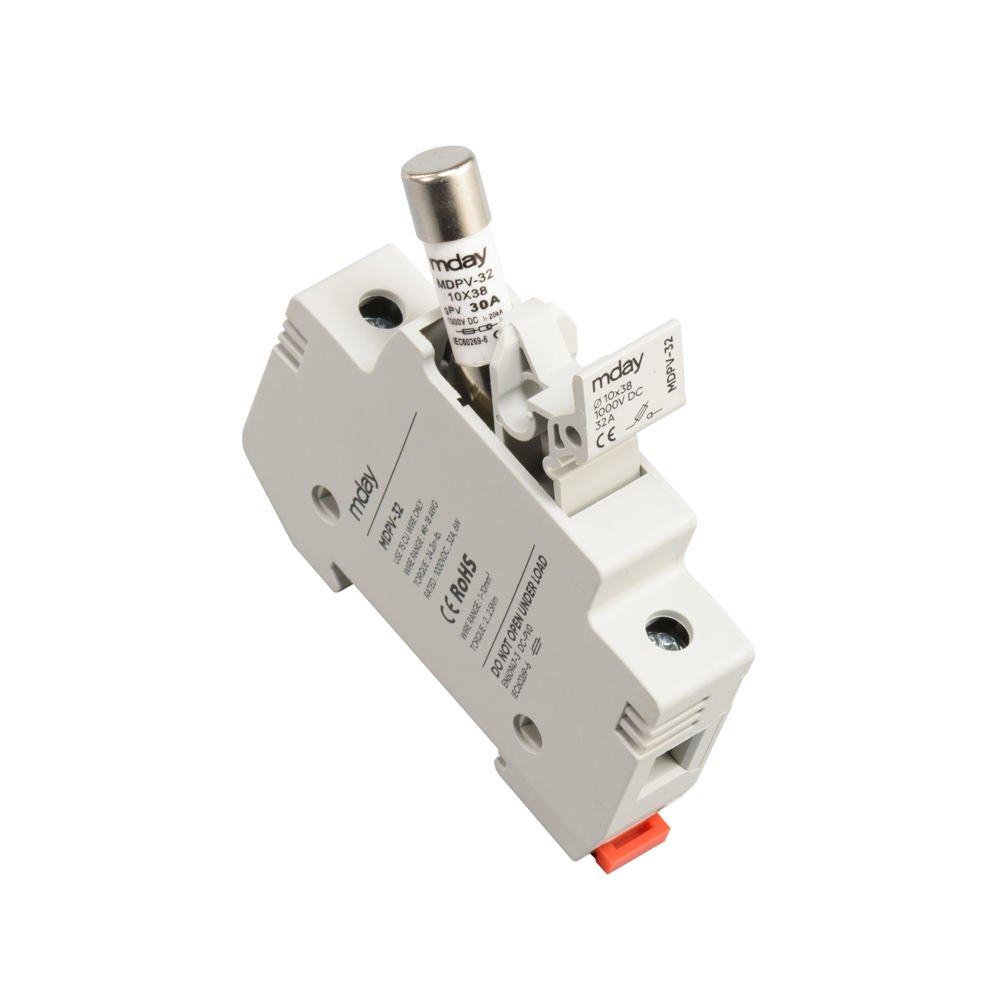
Fuse Bases:
Fuse bases are used to hold the cylindrical fuses and provide the necessary electrical connections. They can be single-phase or multi-phase configurations.
Safety:
Cylindrical fuses are a crucial safety device, protecting electrical equipment and preventing electrical fires or damage caused by overcurrents.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.